Google Analytics: Event Tracking Code Generator
Here are your results
Copy this code and implement on your site: Here's what that implementation might look like:Implementing The Tracking Code On Your Website
The event tracking code generator generates tracking code to track clicks on your WordPress website for SEO.
To implement the event tracking code generator, you need to add the tracking code to the HTML element people are supposed to click to complete the action.
For example, let’s say you want to track the number of page views and clicks on a link on your homepage that points to the pricing page. The tracking ID for that on your web page might look something like this:
Once you add google analytics tracking code to that link, the HTML code snippet might look something like this:
Configuring Your Events As Goals in Google Analytics
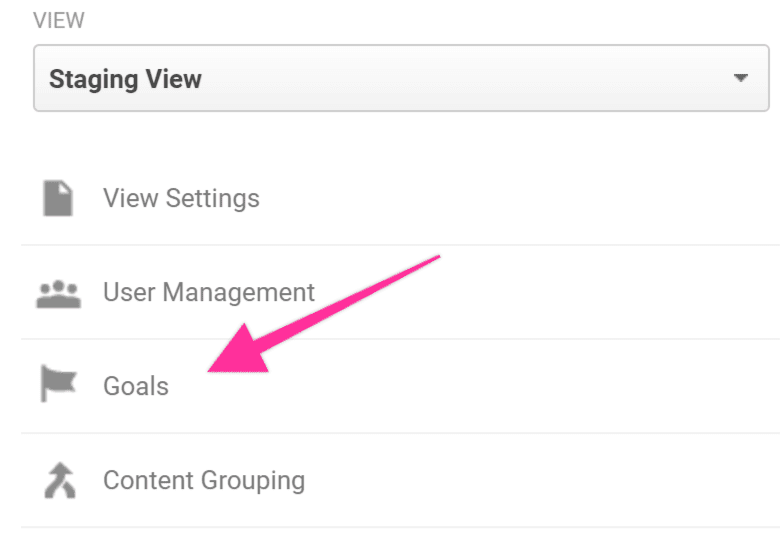
Log into your Google Analytics and click “Admin” in the sidebar.
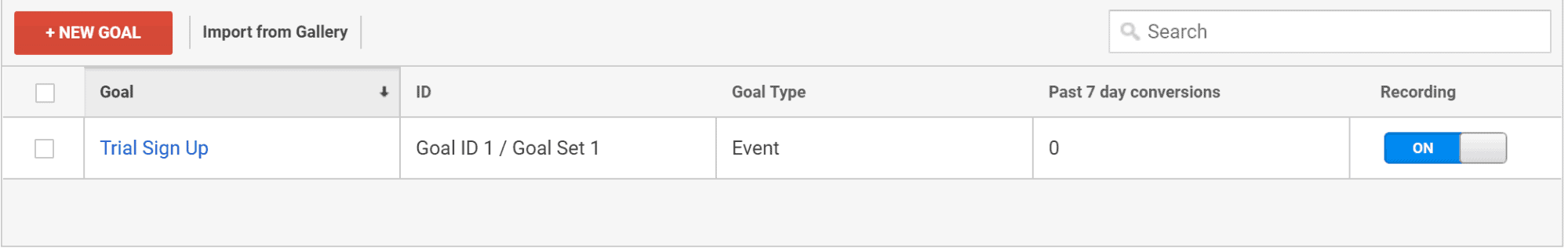
Select the correct Google Analytics Account, Property, and View. Then, click “Goals” under the “View” column.
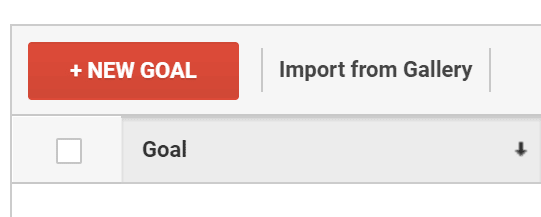
Click “New Goal.”
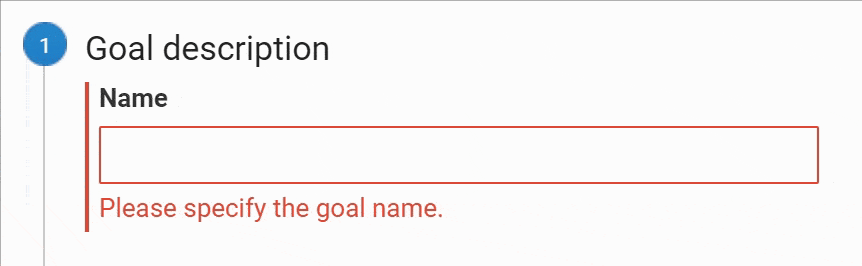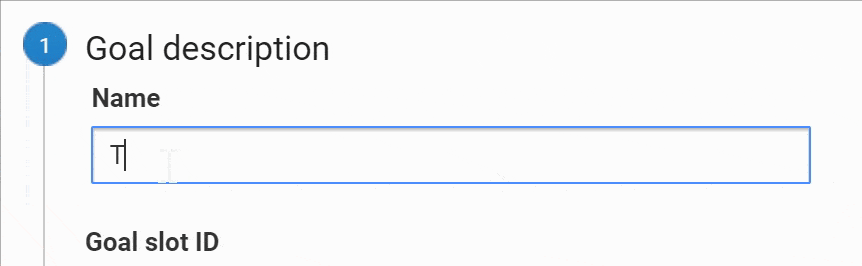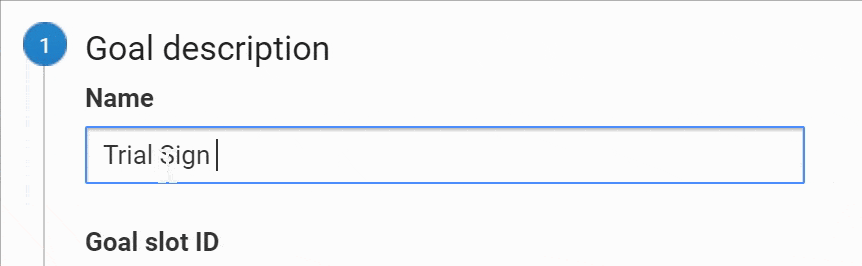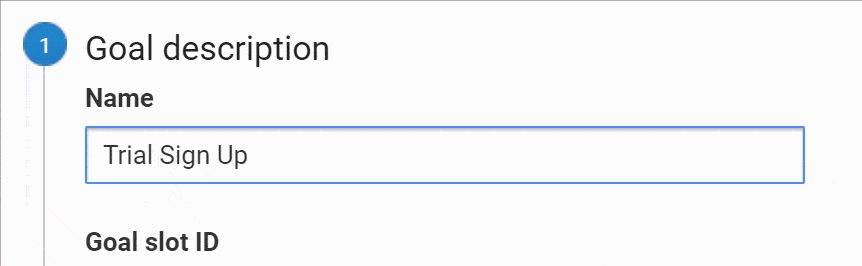
Select a custom goal and name your Goal. Use something short and intuitive, it should be obvious for you or anyone what it is about since this name will appear on your reports.
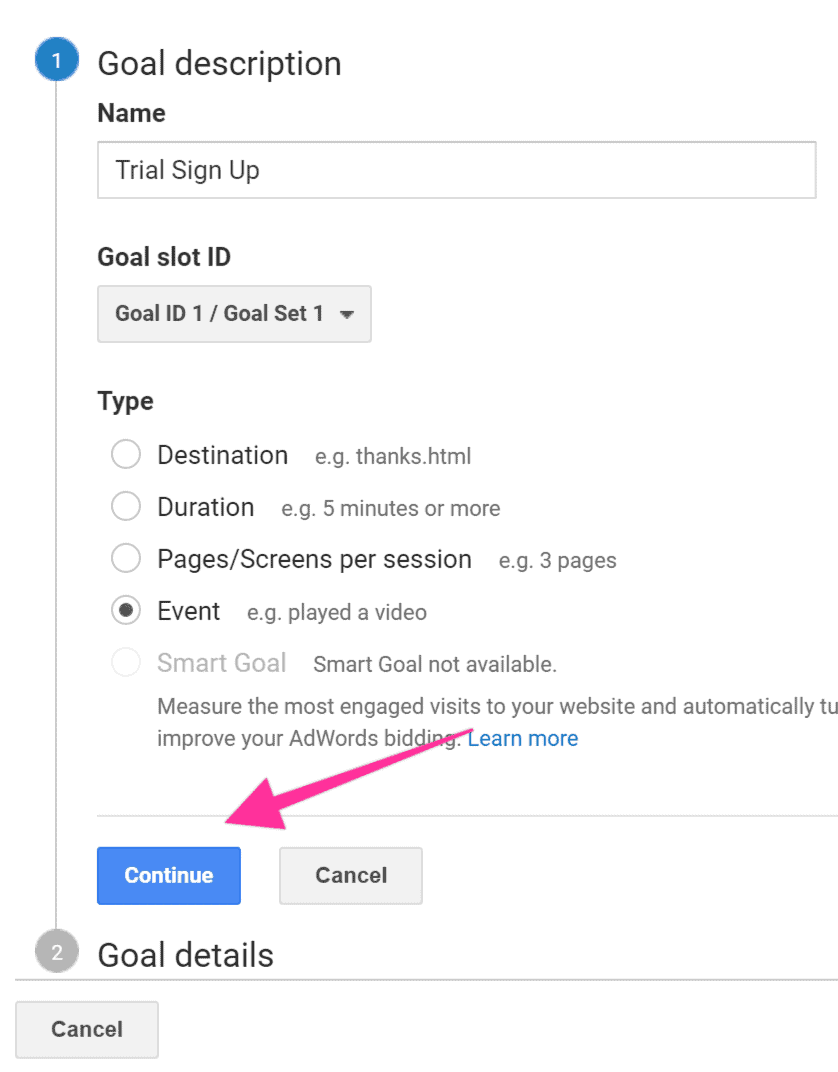
Select your preferred Goal ID and Goal Set slot (if you don’t have any Goals yet, leave the default option). Select “Event”, and click “Continue.”
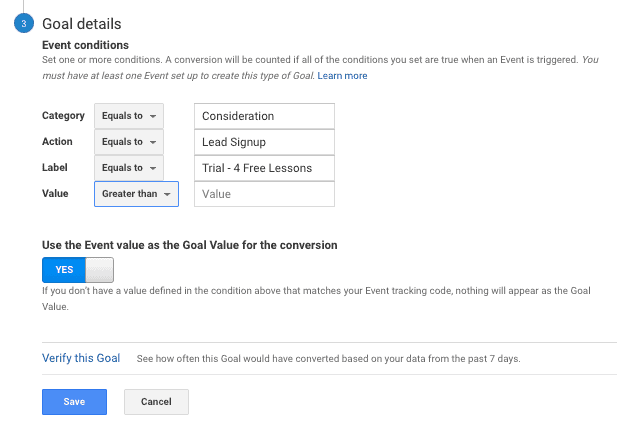
Enter the same values for the “Category”, “Action”, and “Label” that you added on the tool above, and make sure all dropdowns are set to “Equal to." Leave “Value” blank.
Finally, click “Save” and you should see the Goal you have just created, make sure the “Recording” toggle is set to “On.”
Testing Your Google Analytics Goals
First, install the Google Tag Assistant Chrome extension on your Google Chrome browser. This tag assistant helps to verify Google tags like Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager (GTM) on your web page.
Open your website using Chrome, click on the Google Tag Assistant icon extension and click “Record.”
Click on the element that’s supposed to trigger your goal.
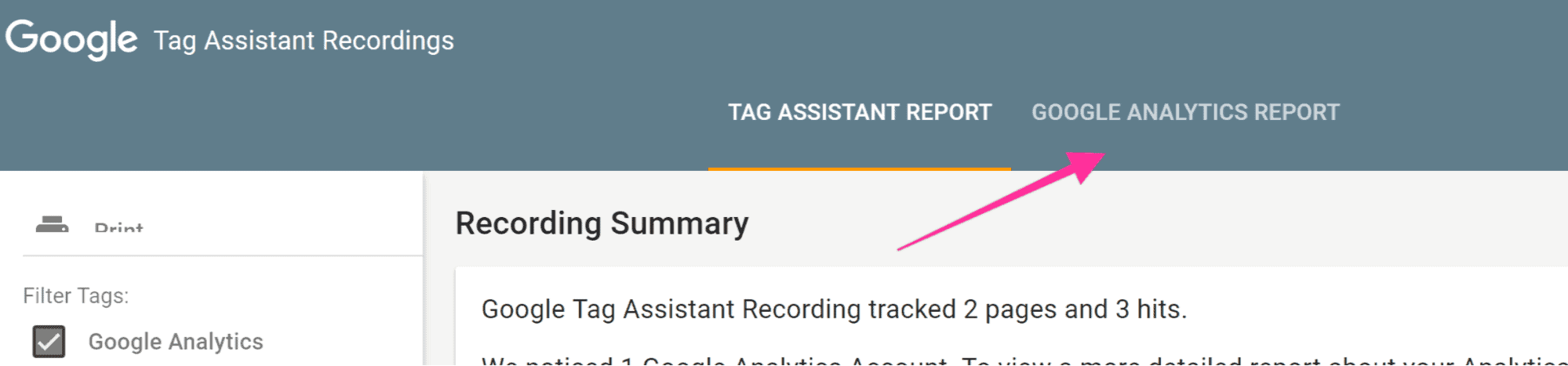
Click on the Google Tag Assistant Chrome extension again and click “Stop Recording” and then click “Show Full Report.”
Select “Google Analytics Report.”
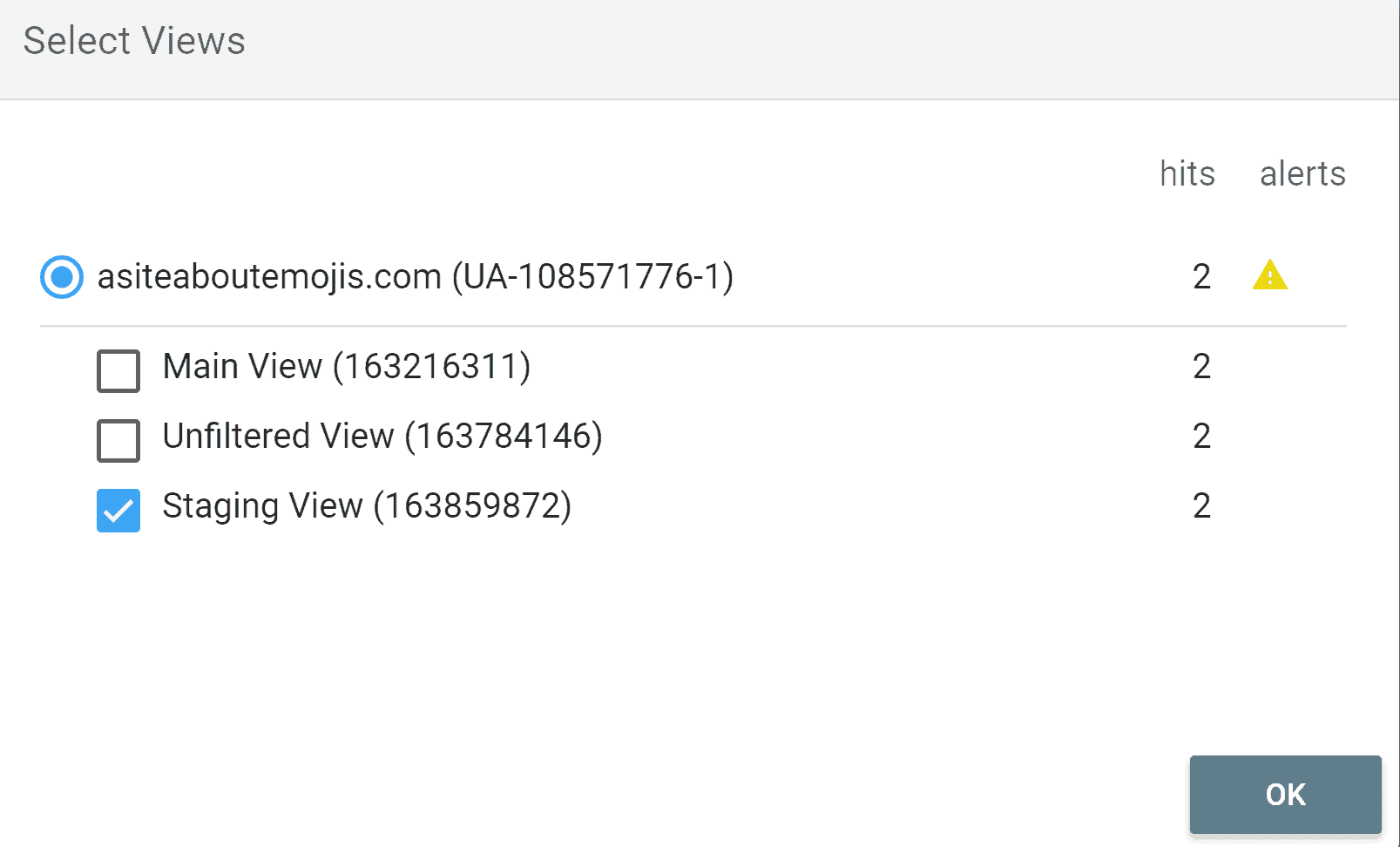
Select the view that you want to test and click “Ok.”
Scroll down until you find the “Conversions” section, you should be able to see the name of your Goal, your Conversion Value, and a green tick after it.

Additional Resources
Get a FREE Digital Marketing Strategy For Your Business or Your Clients — In Under 5 Minutes
No credit card required.